The digital signature is the unforgeable equivalent of the handwritten signature. Provided that the digitally generated signatures also comply with the regulations prescribed in the eIDAS Regulation. Then the digital signature is not only forgery-proof, but also 100% legally valid.
For many people, however, the topic still raises questions and uncertainty. Is my signature secure? Can my signature be forged? How can I make sure the right person has signed?
In order to be able to answer these and other questions, in this article we will deal with how a document can be validly digitally signed and what is necessary for this.
This allows an electronic document to be digitally signed securely
Disambiguation:
Digital signatures are used to approve and validate documents in electronic form. They use complex cryptographic mechanisms to authenticate digital documents and messages, confirm the identity of signers, and protect data from tampering and tampering during transmission.
Digital signatures are equipped with backend tools to ensure that only an authorized person can sign a document and to prevent changes after signing.
A digital signature is generated using a unique digital identifier called a “digital certificate” or “public key certificate.” Digital certificates are issued by accredited certificate authorities (CAs) after verifying the identity of the applicant.
- A Certification Authority (CA) is an entity that is authorized to issue digital certificates. It acts as a trusted third party (TTP) that verifies the identity of the holder of a certificate. A certificate authority also certifies the possession of a public key.
- A digital certificate is an electronic passport that identifies the participant in a PKI-secured conversation and allows individuals and institutions to securely share data online. The encryption and decryption of data is done with a pair of public and private keys.
- A public key is a unique numeric identifier used to encrypt data or verify digital signatures. It is issued by a certification body to a person or organization and is publicly available to anyone who needs it.
- A private key is known only to its owner. It is used to decrypt data created with the corresponding public key or to generate digital signatures.
Digital signatures and digital certificates are closely linked. Your applications and usages depend on how these systems are implemented and how the PKI infrastructure works. A digital certificate is sometimes referred to as a digital signing certificate because it confirms the public key (authenticity) of the signing authority.
Why do I need a digital signature and certificate?
Let’s start with a simple example. Alice and Bob want to communicate together or sign a document.
Scenario 1: Introductory example
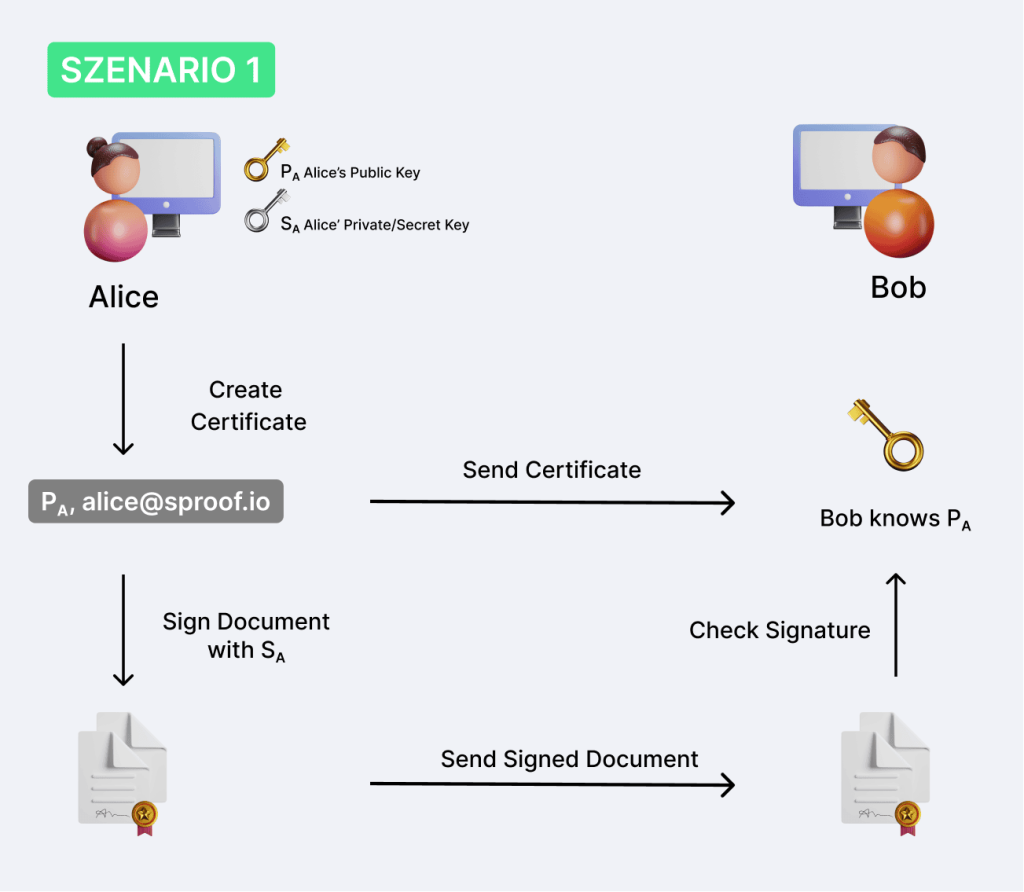
Alice has two digital cryptographic keys – a Public (PA) and a Private/Secret (SA) key. The public key may be passed on. The private key, however, must be kept secret and kept safe by Alice.
Alice creates a digital certificate that contains her public key and email address. She sends this certificate to Bob to share her public key with Bob.
Alice can now sign a document with her private key and send it to Bob. Bob can then check that Alice’s public key matches the signature made with Alice’s private key.
Private and public key are therefore two sides of the same coin. Anything signed with a private key can be verified with the appropriate public key.
This now ensures that only Alice can make a signature with her private key.
However, another security measure must be introduced.
It must be ensured that the linking of Alice Public Key and her user ID (e.g. e-mail address) is really checked.
Scenario 2: What can happen if the certificate is not verified?
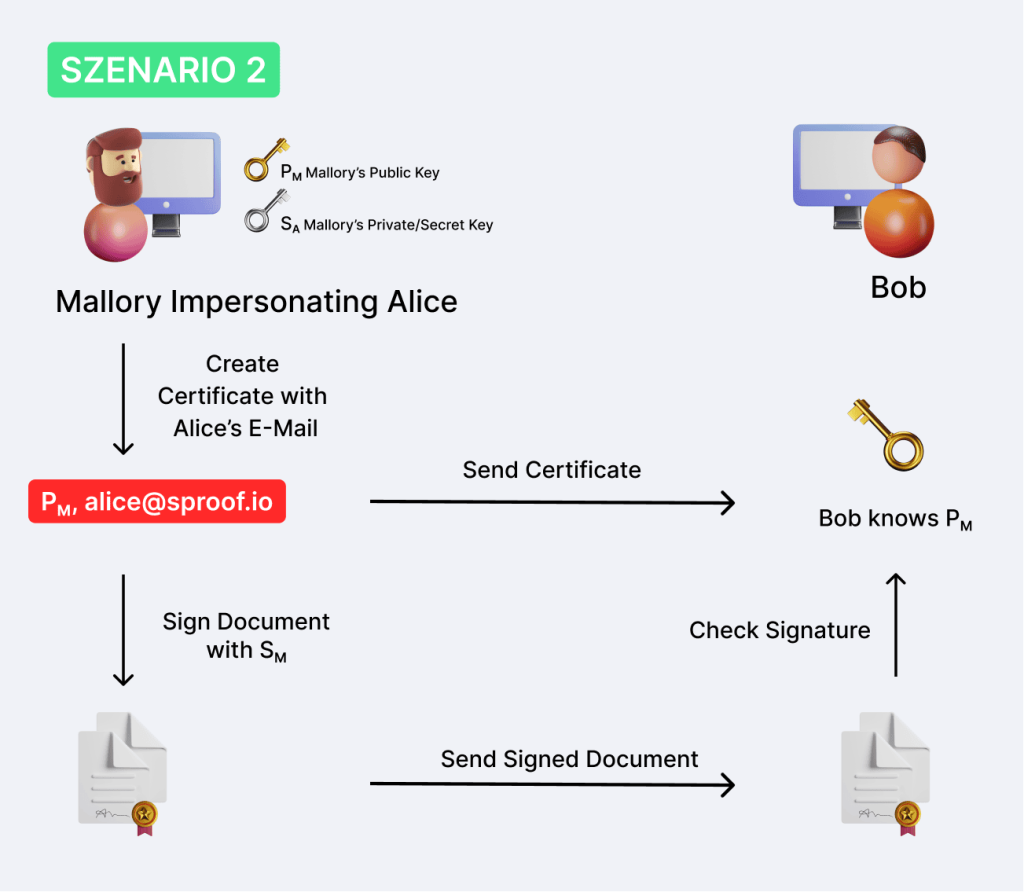
This time, Mallory wants to pretend to be Alice and communicate with Bob. Mallory has neither Alice’s nor Bob’s private key. However, he has his own private-public key pair.
Mallory tries to convince Bob that his private key belongs to Alice. To do this, he builds a certificate himself from his public key and Alice’s e-mail and sends it to Bob. He thinks he has received the public key from Alice.
Now Mallory can sign documents with his private key and send them to Bob without hindrance. The user can check the signature again with the public key and match which ones again. Bob is now convinced that Alice signed this message. In reality, however, it was Mallory.
The problem here is that Mallory has a chance to create a link between his public key and Alice’s user ID.
However, we want to prevent that and for that we need a third party.
Scenario 3: How to do it correctly?
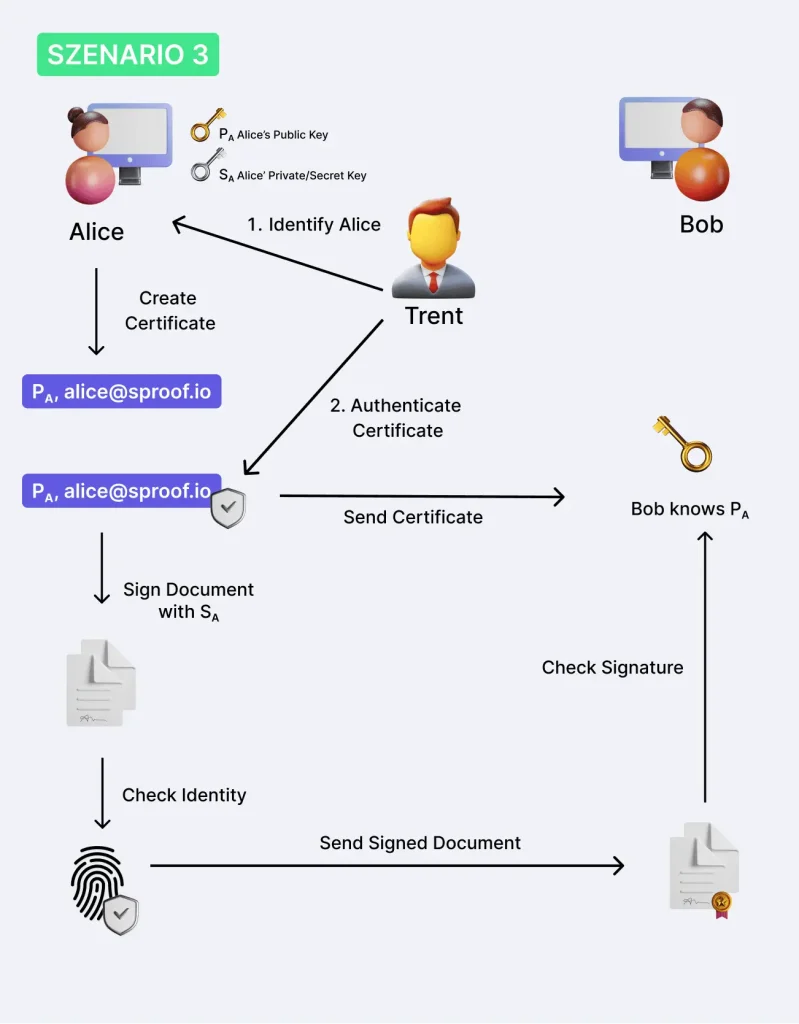
Trent is a trusted third party that ensures that the linking of Alice Public Key and her user ID is verified. Trent verifies Alice’s identity, e.g. by means of ID control with Video Ident, and certifies the digital certificate.
Alice can now sign messages and Bob can be sure that the message really comes from Alice. This will enable us to produce forgery-proof digital signatures!
Two things are therefore important:
- On the one hand, Alice’s identity must be established and her UserID must be linked to a public key. Alice always has the private key in safe custody. Either by yourself or through a secure third-party provider such as sproof.
- Secondly, when a signature is made, the identity of the signatory must be verified, for example by means of a push message on your mobile phone.
This enables us to produce digital, qualified signatures that are at least as secure as analogue signatures.
Technically, each digital signature created for a particular document is unique and therefore extremely difficult to forge. The ability of digital signatures to ensure the integrity and authenticity of electronic documents while indicating signer consent allows businesses, contractors, and customers to interact online and share information securely.
Technically, each digital signature created for a particular document is unique and therefore extremely difficult to forge. The ability of digital signatures to ensure the integrity and authenticity of electronic documents while indicating signer consent allows businesses, contractors, and customers to interact online and share information securely.

Digression: Who are Alice, Bob and Mallory?
Alice, Bob and Mallory are fictional characters who serve as synonyms for the main players in communication and data sharing. Instead of speaking of anonymous individuals, these individuals are personified through the use of Alice, Bob, and Mallory. This method facilitates the presentation of complex relationships and processes and makes them more understandable for the reader.
Who are Alice and Bob?
Alice and Bob are representative figures for the participants in a communication between two parties. Alice acts as the initiator who establishes the communication. Bob takes on the role of the person who takes the message. Most of the time, Alice strives to deliver a message to Bob while Bob waits for the message from Alice.
Who is Mallory?
Mallory is an active attacker of a communication who is not afraid to intervene in the communication to manipulate messages or change data. As a man-in-the-middle (MITM), Mallory is particularly dangerous for Alice and Bob, who are able to protect themselves from him with the help of cryptography.
Without the application of cryptography …
- … data transmissions are susceptible to manipulation by third parties. Mallory could, for example, use intercepted data for its own purposes or change it unnoticed.
- … Mallory could impersonate another person and gain access to confidential information.
- … Alice could claim undetected that certain data was falsified by Mallory.
However, it is important to emphasize that
- … cryptography is NOT able to prevent Mallory from altering or intercepting data unnoticed.
- … that the interruption or prevention of connections is not excluded.
- … The use of cryptography is nevertheless an important protective mechanism to minimize the risk of data manipulation.
Who is Trent?
Trent, derived from the English “trusted entity”, is a trusted third party. For example, as a Certificate Authority, or CA for short.




